Abstract
The circulation and supply system of elastic supply tokens is constantly changing. The core idea is to adjust the token supply through rebasing rather than relying on price fluctuations.
Imagine if the Bitcoin protocol reached a target price by adjusting the number of Bitcoins in a user's wallet. So, let's say you own 1 BTC today. When you wake up tomorrow, you may have 2 BTC, but each will be worth half of what it was yesterday. This is how the rebasing mechanism works.
Introduction
Decentralized finance (DeFi) promotes the explosion of new financial products in the blockchain field growth. We have previously introduced liquidity mining, tokenized Bitcoin in Ethereum, Uniswap and flash loans. Another hot topic in the cryptocurrency field is elastic supply tokens, also known as "rebasing tokens."
The unique mechanisms behind them can support a large number of experiments. Let’s take a closer look at how these tokens work.
What is an elastic supply token?
Elastic supply (or rebasing) tokens work roughly like this: the circulating supply of tokens increases and decreases as the price rises and falls. The increase or decrease in supply is achieved through a mechanism called "rebasing". After performing a rebase, the supply of each token will be algorithmically increased or decreased based on the current price.
From some perspectives, elastic supply tokens are similar to stablecoins. The goal of both is to stabilize the target price, and this rebasing mechanism helps achieve that goal. However, the main difference between the two is that rebasing tokens work through supply (elasticity) changes.
You may ask, isn’t the supply of many cryptocurrencies changing? indeed so. Currently, 6.25 new coins are mined per Bitcoin block. After the halving in 2024, this number will drop to 3.125 coins/block. This ratio is predictable and we can estimate the number of Bitcoins in the market next year or after the next halving.
Elastic supply tokens work differently. As mentioned earlier, the rebasing mechanism periodically adjusts the circulating supply of tokens. Let’s say some elastic supply token wants to achieve a stable price of $1. If the price exceeds $1, the supply will be increased through a rebasing mechanism, reducing the value of a single token. Conversely, if the current price is below $1, this will reduce the supply and increase the value of each coin.
What does this mean in practice? If a rebase is performed, the number of tokens in the user's wallet will change. Let’s say we hold rebased USD (rUSD), a hypothetical token with a target price of $1. You deposit 100 rUSD in your hardware wallet. Suppose the currency price falls below $1. After performing the rebase, you will only have 96 rUSD left in your wallet. At the same time, the value of each account has increased accordingly.
The core principle of this kind of token is that the user's currency holdings maintain a certain ratio with the total supply and will not change due to rebasing. Let's say you hold 1% of the total token supply before rebasing. Even if the number of tokens in your wallet changes after rebasing, you still own 1% of the total supply. Essentially, your share of the tokens held in the network does not change no matter how the price changes.
Token rebasing example
Ampleforth
Ampleforth is the first elastic supply one of the tokens. It hopes to become a non-collateral synthetic commodity with a target price of $1 for 1 AMPL. Rebase is performed every 24 hours.
Before the launch of the liquidity mining activity called "Geyser", the project had relatively little appeal. What is particularly interesting about this package is its duration. It will continue to distribute tokens to participants for 10 years. Geyser is a classic example of creating huge traction for DeFi projects through liquidity incentives.
From a technical perspective, this is a stablecoin, and the AMPL price chart illustrates the volatility of the elastic supply token.

AMPL has a price target of $1, but the price could fluctuate wildly.
Please note that this price chart only shows the unit price of AMPL tokens and does not take into account supply changes. Even so, given the massive volatility, Ampleforth is likely to be a high-risk coin.
It may make more sense to evaluate elastic supply tokens from a market capitalization perspective. Since the unit price of a token is irrelevant, market capitalization can be a barometer of a network's growth and appeal.
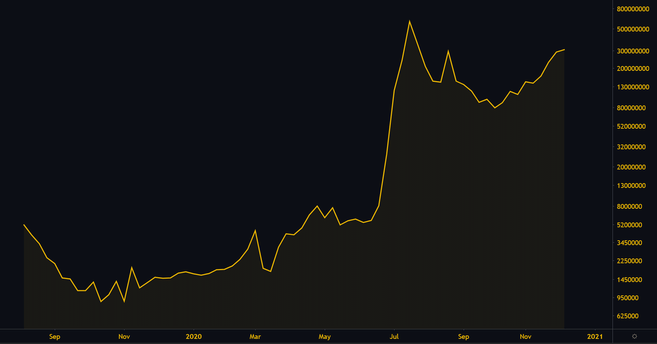
AMPL’s exponential market capitalization.
Yam Finance
Yam Finance is another elastic supply token project that has attracted widespread attention. The overall design of the Yam protocol is somewhat similar to the combination of Ampleforth's elastic supply, Synthetix's staking system and Yearn.finance's fair issuance. YAM also aims to stabilize the price at $1.
YAM is an experiment completely run by the community, and all tokens are issued through liquidity mining. There is no pre-mining or founders distribution – even everyone can enjoy the dividends of token creation through the liquidity mining program.
As a brand new and unknown project, YAM locked US$600 million in value into the pledge pool in less than two days. The reason why such a high liquidity value is brought together is because the YAM pool is tailor-made for holders of some popular DeFi tokens. These tokens include COMP, LEND, LINK, MKR, SNX, ETH, YFI and ETH-AMPL Uniswap LP tokens.
However, there may be loopholes in the rebasing mechanism, causing the supply of tokens to be mined to increase. With the joint efforts of the community, the project used funds to complete the audit, and was eventually relaunched and migrated to a brand new token contract. Today, the future of YAM is entirely in the hands of YAM holders.
Risks of Flexible Supply Tokens
Flexible Supply Tokens are a very dangerous investment with great risks . Be sure to understand it before investing money. Note that looking at the price chart won't help as your token holdings will change after rebasing.
Of course, everything is possible whether the income will increase or decrease. If a rebasing occurs when the currency price drops, in addition to losing money on the decline, each rebasing will reduce the tokens in your hand!
Their mechanics are difficult to understand, so investing in rebased tokens is likely to result in losses for most traders. Investing in elastic supply tokens can only be done if you fully understand the mechanics behind them. Otherwise, you won't have full control over your investment and can't make informed decisions.
➟ Want to start a digital currency journey? Go to Binance and buy Bitcoin now!
Summary
Flexible supply tokens are one of the noteworthy innovations in the DeFi field. As we have seen, these currencies and tokens can all algorithmically adjust their supply in an attempt to reach a target price.
Are elastic supply tokens just a fun experiment, or can they create significant traction and carve out a niche market? Everything is still unknown. But what is certain is that there are some new DeFi protocols being developed that are moving towards this goal.


 Forum
Forum Finance
Finance
 Specials
Specials
 On-chain Eco
On-chain Eco
 Entry
Entry
 Podcasts
Podcasts
 Activities
Activities
 OPRR
OPRR
