Chapter
- Introduction to Bitcoin
- Where does Bitcoin come from?
- Start using Bitcoin
- Bitcoin Halving
- Common Misunderstandings
- Bitcoin Scaling Capability
- Participate Bitcoin Network
Chapter 1: Introduction to Bitcoin
Content Introduction Overview
- What is Bitcoin?
- What are the uses of Bitcoin?
- What is the value of Bitcoin?
- How does the Bitcoin system work?
- What is blockchain?
- Is Bitcoin legal?
- A brief history of Bitcoin
- Who invented Bitcoin?
- Did Satoshi Nakamoto invent blockchain technology?
- Digital currency before Bitcoin
Bit What is a coin?
Bitcoin is one of the forms of digital cash. Unlike common fiat currencies, Bitcoin is not controlled by any central bank; the financial system it belongs to is run by thousands of computers around the world, and anyone who wants to participate only needs to download open source software.
As the first digital currency, the concept of Bitcoin was proposed in 2008 (released in 2009). It gives users the ability to send and receive digital currencies (abbreviated as "BTC" in English), but the more eye-catching features of Bitcoin are: censorship resistance, funds cannot be used twice, and transactions can be conducted anytime and anywhere.
What are the uses of Bitcoin?
Everyone’s starting point for using Bitcoin is different. Many people like its license-free feature, that is, anyone can send and receive as long as they are connected to the Internet. Bitcoin is a bit like cash in terms of unrestricted use; but Bitcoin's digital form means it supports cross-border transfers.
What is the value of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is decentralized, censorship-resistant, secure and borderless.
Based on the above characteristics, the advantageous use cases of Bitcoin include international remittances and payments, effectively protecting personal identity privacy (using debit or credit cards can easily expose personal identity information).
Many people will not spend Bitcoin, but choose to hold it for the long term (i.e. HODL). The number of Bitcoins is limited, so it is called "Digital Gold". Some investors regard Bitcoin as a "store of value," which is as rare and difficult to "mine" as precious metals such as gold and silver.
Coupled with the global versatility and high liquidity of Bitcoin, long-term currency holders believe that Bitcoin is an ideal medium for long-term storage of wealth and will increase in value over time.
How does the Bitcoin system work?
In the Bitcoin system, the way funds are sent is not the digital transfer of cash as most people imagine. If Alice transfers money to Bob, the process is more like Alice recording that she transferred $1 to Bob on a ledger visible to anyone. If Carol wants to charge Bob $1, she can see from the same ledger that Bob does have $1.
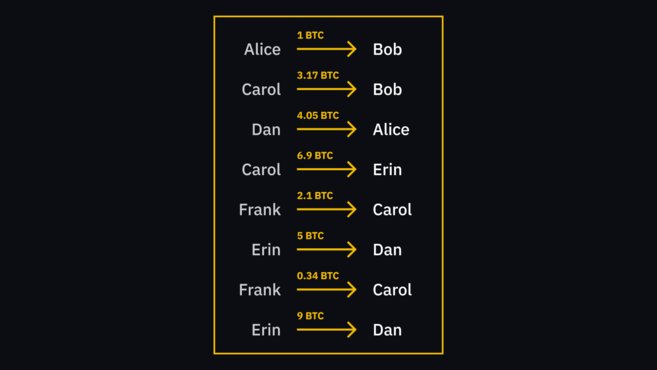
The ledger here is the so-called "blockchain" database. All participants share the same copy of the data; this copy is stored on the participant's device and data updates are synchronized across all connected devices.
When a payment occurs, the relevant information is broadcast directly to the peer-to-peer network; there is no central bank or institution involved in the payment process. The Bitcoin blockchain uses a unique "mining" mechanism to add new information, such as concatenating new blocks with transaction information on the chain.
What is blockchain?
The blockchain is an append-only ledger, that is, it only accepts data additions. Once information is added to the blockchain, it is difficult to modify or delete. To ensure this, the blockchain imposes a pointer in each block that points to the next connected block.
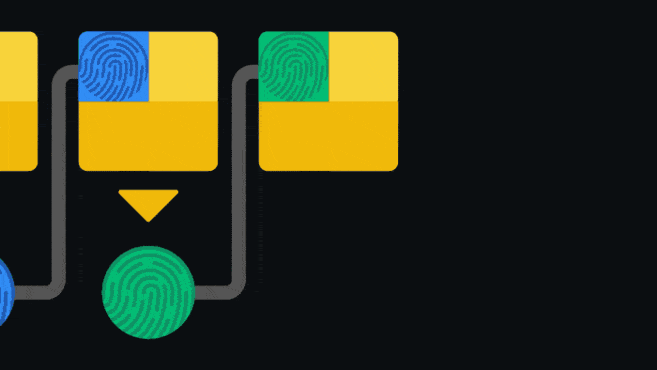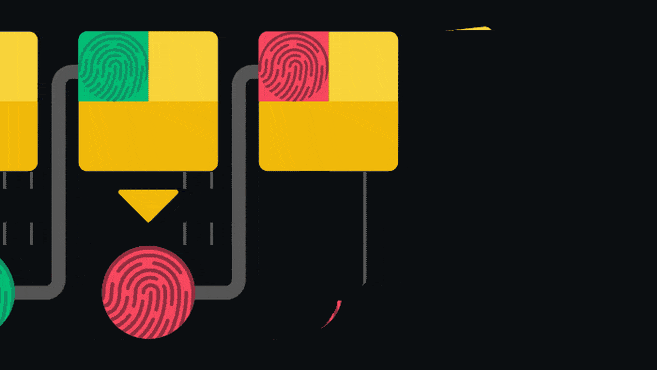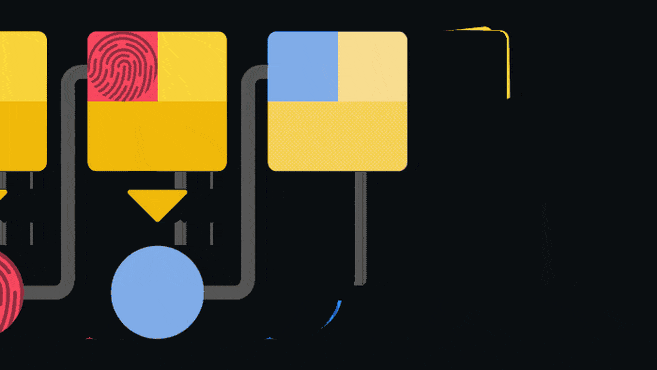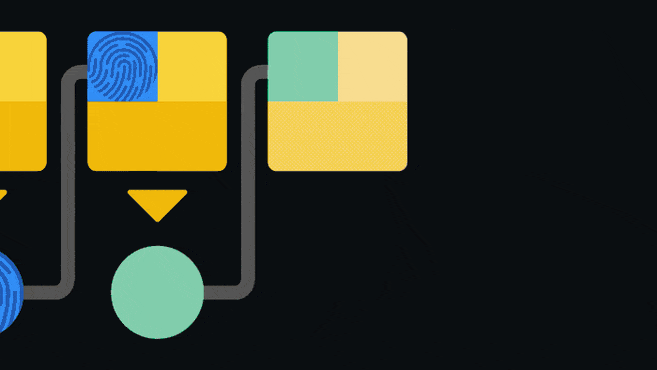
The pointer is actually the hash value of the previous block. Hashing (also known as "hashing") is inputting data into a set of one-way functions to obtain a corresponding special "fingerprint". Changing the input values even slightly will result in a completely different fingerprint. Since blocks are connected like a chain, changes to any block will invalidate all subsequent blocks. Such an architecture is one of the security guarantees of the blockchain.
If you want to learn more about blockchain, please check out the "Blockchain Technology Beginner's Guide".
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin is completely legal in most countries, with a few exceptions. Nonetheless, it is important to understand the relevant laws in your jurisdiction before investing.
In areas where Bitcoin is legal, government agencies adopt various relevant taxes and regulations. Overall, controls in this area have not yet been developed and perfected, and significant changes are likely to occur in the future.
A brief history of Bitcoin
Who invented Bitcoin?
No one knows! The inventor of Bitcoin, "Satoshi Nakamoto," is actually a pseudonym, and his true identity remains a secret. Satoshi could be a person or a group of developers, and could come from anywhere in the world. Although "Satoshi Nakamoto" is a Japanese name, his English skills are very strong, leading many people to conclude that she/he/they come from an English-speaking country.
Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin white paper and software, but mysteriously disappeared in 2010.
Did Satoshi Nakamoto invent blockchain technology?
In fact, many of the technologies involved in Bitcoin have existed for some time. The concept of blockchain was not born because of Bitcoin. The immutable data structure can be traced back to the early 1990s. At that time, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta conceived a system for adding timestamps to files. It relies on encryption technology to ensure data security and avoid tampering, much like today's blockchain.
Interestingly, Satoshi Nakamoto’s white paper did not mention the term “blockchain”.
You may wish to check out "History of Blockchain".
Digital currency before Bitcoin
Bitcoin is not a digital currency The first, but definitely the most successful. Past attempts laid the foundation for Satoshi's invention.
DigiCash
In the late 1980s, DigiCash was founded by cryptographer and computer scientist David Chaum to launch a privacy-centered online transaction solution. The scheme is based on a paper written by David Chaum (details here).
DigiCash's model is a centralized system, but it is not an interesting experiment. The company later went bankrupt, with Chaum blaming the lack of e-commerce at the time.
B-money
In the 1990s, the concept of B-money first appeared in a proposal by computer engineer Dai Wei. The proposal was subsequently cited in the Bitcoin white paper, and it’s easy to see why.
The B-money proposal involves a "proof of work" system (applied to Bitcoin mining) and a distributed database for transaction signing. The second version of B-money also describes a concept similar to the mortgage mechanism used by other digital currencies.
Although B-money ultimately stopped at the drafting stage, it is not difficult to see its impact on Bitcoin.
Bit Gold
Bit Gold is so similar to Bitcoin that some people believe that Nick Szabo, the founder and computer scientist of the former, is Nakamoto Cong. At its core, Bit Gold is a ledger that records strings of data calculated by proof of work.
Like B-money, Bit Gold has not been developed. However, Bit Gold has many commonalities with Bitcoin that solidify the former’s pioneering status.
Chapter 2: Where did Bitcoin come from?
Content Tour
- How are Bitcoins generated?
- What is the total amount of Bitcoin?
- How does Bitcoin mining work?
- How long does it take to create a block?
How are Bitcoins generated?
Bitcoin has a limited supply, but only some of it enters circulation. The only way to generate new coins is "mining", a unique mechanism for adding data to the blockchain.
What is the total amount of Bitcoin?
The Bitcoin protocol sets the maximum supply of Bitcoin at 21 million. As of 2020, nearly 90% of Bitcoins have been "mined", but the remainder will take 100 years to be fully mined. The reason is the "halving" event that occurs in the cycle, which gradually reduces the mining bonus.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Mining is the way to add new blocks to the blockchain. Participants must devote their computing power to solving cryptographic puzzles. To attract miners, anyone who proposes a valid block will be rewarded.
Although the cost of creating a block is high, the cost of checking a block is very low. If someone attempts to cheat and submit an unqualified block, the request will be immediately rejected by the network, and the miner will not be able to recover the mining cost.
The bonus earned from mining is generally called "block reward" and consists of two parts: the transaction fee and the mining bonus. Mining bonuses are the only source of new Bitcoins. Every time a block is generated, the total supply of Bitcoin increases by a fixed amount.
How long does it take to create a block?
The Bitcoin protocol will flexibly adjust the mining difficulty to control the block generation time to about 10 minutes. The creation time between two connected blocks is not necessarily exactly 10 minutes, but fluctuates around this value.
Chapter 3: Getting Started with Bitcoin
Content Tour
- How to buy Bitcoin?
- How to buy Bitcoin with credit/debit card
- How to buy Bitcoin on peer-to-peer market
- Bitcoin can be used What to buy?
- Where can Bitcoin be spent?
- What should I do if I lose my Bitcoin?
- Can Bitcoin transactions be reversed?
- Can Bitcoin be used to make money?
- How to store Bitcoin?
- Store in Binance
- Store in Bitcoin wallet
- Hot wallet
- Cold wallet
How to buy Bitcoin?
How to buy Bitcoin with a credit/debit card
With the Binance platform, You can buy Bitcoin seamlessly on your web browser. The method is:
- Log in to the digital currency buying and selling portal.
- Select the purchase currency and payment currency.
- Log in to your Binance account; those who do not have an account must register first.
- Select a payment method.
- Enter bank card information as prompted, and then complete identity authentication.
- Done! The corresponding Bitcoins will be recorded on your Binance account.
How to buy Bitcoin on peer-to-peer markets
You can also Buy and sell Bitcoin on the peer-to-peer market. With the Binance Mobile App, you can buy Bitcoin directly from other users. The method is:
- Open the APP, then log in or register an account.
- Select “One-click currency exchange“, and then click “Purchase” in the upper left corner of the interface.
- Select one of the transaction types that pops up and click “Buy “.
- You can pay with other digital currencies (click “Digital Currency Payment”) or pay with fiat currency (click “Fiat Currency Payment” ).
- Next, you will be asked to specify a payment method.
- Select “Buy BTC”.
- At this point, you need to pay. When finished, click “Mark as Paid” and Confirm.
- The transaction is completed when the seller sends the BTC to you.
Want to get started with digital currencies? Come to Binance to buy Bitcoin!
What can Bitcoin be used to buy?
Bitcoin can be used to buy many things. It is currently difficult (though not impossible) to identify brick-and-mortar merchants that accept Bitcoin. You may wish to search online. Some websites accept Bitcoin payments; some will allow customers to purchase gift cards with Bitcoin first and then use the gift cards to pay for services.
The following are examples of items that can be purchased with Bitcoin:
- Plane tickets
- Hotel rooms
- Real estate li>
- Food & Drinks
- Clothing
- Gift Cards
- Online Subscriptions
Where can Bitcoin be spent?
There are more and more places to spend Bitcoin! Let’s look at a few examples.
TravelbyBit
Don’t want to worry about huge credit card fees when traveling around the world? Why not use digital currencies such as Bitcoin to book flights and hotels on TravelbyBit. Register and use digital currency to enjoy a 10% discount.
Spendabit
The search engine Spendabit can help you find "Bitcoin-friendly" products. You just enter what you want to buy and the system will find a list of merchants that accept Bitcoin payments.
Coinmap
Coinmap can locate digital currency merchants and ATMs in your area. If you’re eager to find a place to spend your Bitcoin, this platform is ideal for you.
Bitrefill
Here you can use digital currencies such as Bitcoin to purchase gift cards for a wide variety of services or recharge phone bills. The program is easy to use and you can also pay using the Lightning Network.

Heat map of retailers paying in digital currencies. Source: https://coinmap.org/
What to do if you lose your Bitcoins manage?
Since the Bitcoin network does not have a bank, users are responsible for the security of their own assets. Some people host their assets on exchanges, while others choose various types of wallets. Wallet users must write down their mnemonic phrase so that they can retrieve their wallet information when needed.
Can Bitcoin transactions be reversed?
Once data is added to the blockchain, it is very difficult (in fact almost impossible) to remove it, meaning transactions entered into cannot be undone. Before transferring money, please remember to double-check whether the receiving address is correct.
If you want to understand the theoretical method of reversal trading, you can read "What is a 51% attack?" 》
Can Bitcoin be used to make money?
Bitcoin can be used to make money or lose money. Generally speaking, long-term investors believe that Bitcoin will appreciate in value in the future, so they will buy and hold the currency for a long time. Some people choose to actively trade between Bitcoin and other digital currencies to make short- to medium-term profits. Both strategies involve risks, but the rewards are often greater than with lower-risk investments.
Some investors adopt a comprehensive strategy: holding Bitcoin as a long-term investment and opening a separate investment portfolio for short-term trading. Because investors have different risk appetites and goals, there is no right or wrong way to allocate assets in a portfolio.
Lending is becoming more and more popular as a way of passive income. Token holders can earn interest income by lending funds to others. Platforms such as Binance Lending allow users to borrow and lend using digital currencies such as Bitcoin.
How to store Bitcoin?
There are many ways to store Bitcoin, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
Stored on Binance
Storage Yes It means that users hand over their digital currency to a third party for safekeeping. They need to log in and send assets to a third-party platform. Exchanges such as Binance often adopt this model, which greatly increases transaction efficiency.
By hosting Bitcoin on Binance, users can easily trade and borrow.
Stored in a Bitcoin wallet
In contrast to custodial solutions, non-custodial solutions represent the user’s control Funds require the use of a "wallet". What the wallet keeps is not the funds themselves, but the keys to unlock the funds on the blockchain. There are two main types of wallets:
Hot wallets
Hot wallets are software that can connect to the Internet, usually in the form of mobile or desktop applications. , convenient for users to send and receive funds. For example, Trust Wallet is an easy-to-operate mobile wallet that supports a wide range of currencies. Hot wallets tend to facilitate payments because they are connected to the Internet, but they are also more vulnerable to attacks.
Cold wallet
A wallet that cannot connect to the Internet is called a "cold wallet". Due to the lack of online attack channels, cold wallets are relatively safer, but the user experience is generally poor. Cold wallet types include hardware wallets and paper wallets. .
If you want to learn more about wallet types, please don’t miss the articleSeveral Common Digital Currency Wallets.
Chapter 4: Bitcoin Halving
Content Tour
- What is the Bitcoin Halving?
- How does the Bitcoin halving work?
- Why does Bitcoin halving occur?
- What is the impact of Bitcoin halving?
- When is the next Bitcoin halving?
What is Bitcoin halving?
Bitcoin halving is actually a reduction in block rewards. After the halving occurs, the new block verification bonus received by miners will be twice less than before, but transaction fees will not be affected.
How does the Bitcoin halving work?
When Bitcoin was first launched, miners received a 50BTC bonus for each valid block they found.
The first halving occurred on November 28, 2012. At that time, the protocol compressed the block reward from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The second halving occurred on July 9, 2016, when the block reward dropped from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC. The next halving is expected to occur in May 2020 and will see the block reward drop to 6.25 BTC.
Perhaps you have also noticed that halvings seem to occur every 4 years, with an error of a few months. This is a result of the protocol architecture design. The protocol does not set a specific date for halving, but stipulates the corresponding block height: Halving occurs every 210,000 blocks. Therefore, it can be estimated that halving occurs every 2,100,000 minutes (block time is about 10 minutes).

From the chart above, you can see the block reward and total supply. How relationships change over time. At first glance, the block reward seems to have dropped to zero, and the maximum supply seems to have entered circulation--which is actually an illusion. The curve is indeed very close to the extreme, but the block reward is not expected to reach zero until 2140.
Why does Bitcoin halving occur?
This is one of Bitcoin’s main selling points, but Satoshi Nakamoto never fully explained why he limited the total supply to 21 million. Some people speculate that 21 million only comes from a simple calculation of the 50 BTC initial block bonus and the 210,000 block halving cycle.
Quantitative supply means the currency is less prone to long-term depreciation. Fiat currency is exactly the opposite: as more and more fiat currencies enter circulation, their purchasing power also weakens.
The mining speed limit is also a reasonable setting. After all, 50% of the total Bitcoin supply was mined before block 210,000 (i.e. before 2012). If block rewards remain unchanged, all Bitcoins will be in circulation by 2016.
The halving mechanism ensures that the mining time can be extended to more than 100 years, giving the system enough time to attract users so that the handling fee market can grow smoothly.
Want to get started with digital currencies? Come to Binance to buy Bitcoin!
What is the impact of Bitcoin halving?
The group most affected by the halving is the miners, because the block reward is the main part of their profits. Halving the block reward means halving the revenue. While fees are not affected, fees to date are still unable to compete with block bonuses.
Therefore, the post-halving block reward may no longer be cost-effective for some miners. No one knows how the entire industry will be affected by this. Reducing block rewards may cause the network to become more centralized and may also promote the efficiency of mining technology.
If Bitcoin continues to rely on the proof-of-work algorithm, fees must be increased to a level that is profitable for miners. This scenario is entirely possible. Since the number of transactions that can be written into a block is limited, if there are too many pending transactions, those with higher fees will be processed first.
As far as past records are concerned, the price of Bitcoin will skyrocket after the halving occurs. Of course, the data available for reference is very limited, because halving has only occurred twice. Many attribute this price movement to Bitcoin’s scarcity resulting in a higher market valuation, a phenomenon triggered by the halving. Supporters of this theory believe that after May 2020, the value of Bitcoin will soar again.
Opponents believe that the market has already considered the halving (see "Efficient Market Hypothesis" for details). The reason is that the halving does not appear suddenly; the participants have already considered it more than ten years ago. We knew that the halving would happen in May 2020. Another argument is that when the first two halvings occurred, the industry was still in the early stages of development; now it has reached scale, mature trading tools exist, and can accommodate more investors .
When is the next Bitcoin halving?
The next halving is expected to be in 2020 When it happens in May, the block reward will drop to 6.25 BTC accordingly. Please pay attention to Binance Academy’s "Bitcoin Halving Countdown" section.
Chapter 5: Common Misunderstandings
Content Navigation
- Are Bitcoin users anonymous?
- Is Bitcoin a scam?
- Is Bitcoin a bubble?
- Does Bitcoin use encryption?
Are Bitcoin users anonymous?
Not entirely. On the surface, Bitcoin users can remain anonymous. In fact, the Bitcoin blockchain is public and anyone can see transactions. A user's identity is not tied to a wallet address on the blockchain, but it is possible for an observer with the appropriate resources to link the two. To be more precise, Bitcoin uses a pseudonym system, where the wallet address is visible to anyone and the user name is kept secret.
Despite this, the privacy of the Bitcoin system is still relatively high. If you want to make it more difficult for observers to pick numbers, there are ways. Free technology exists to create viable privacy barriers by unlinking addresses. In addition, future technology updates will also improve privacy protection - for details, please see the examples in "Introduction to Confidential Transactions".
Is Bitcoin a scam?
No. Like legal currency, Bitcoin can also be used in illegal activities, but this does not mean that Bitcoin itself is fraudulent.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that is not controlled by anyone. Critics label it a "pyramid scheme." In fact, Bitcoin does not actually meet the relevant definition. Whether the value is $20 USD or $20,000 USD, Bitcoin’s functionality as a digital currency is not affected. It has a history of more than 10 years and the technology has proven to be safe and reliable.
However, Bitcoin does suffer from many scams and users should be careful. These include phishing and social engineering scams such as fake portals and airdrops. The general precautions are: If it sounds too perfect, it’s probably a scam. Never tell others your private key or mnemonic phrase, and beware of low-risk, high-return projects. Once funds are sent to a scammer or fake portal, they can never be recovered.
Is Bitcoin a bubble?
The price of Bitcoin fluctuates. No wonder some people call it an "investment bubble." Many economists liken Bitcoin to tulip mania or the dot-com bubble.
Due to the nature of Bitcoin as a decentralized digital commodity, its price is entirely determined by free market speculation. Although the price of Bitcoin is affected by many factors, these factors ultimately drive price trends in the form of market supply and demand. Due to the limited quantity and strict issuance time, the long-term demand for Bitcoin will exceed the supply.
Compared with traditional markets, the digital currency market is smaller. This means that digital assets such as Bitcoin are highly volatile and prone to short-term market supply and demand imbalances.
In other words, Bitcoin prices change from time to time. However, the financial market itself is unpredictable; the total market volume and circulation capacity of digital currencies are still low, and the fluctuations are more obvious.
Does Bitcoin use encryption?
No. Many people do think so, but the Bitcoin blockchain does not use encryption; transactions need to be visible to every node in the network to ensure that the transaction is valid. However, the Bitcoin system uses digital signatures and hash functions. Although some digital signature algorithms involve encryption, Bitcoin does not fall into this category.
It is worth noting that many applications and digital currency wallets use encryption and passwords to ensure account security; however, encryption is not related to blockchain, but many projects integrate the two.
Chapter 6: Bitcoin Scaling Capability
Content Navigation
- What is the expansion capability?
- Why does Bitcoin need to expand?
- How many transactions can the Bitcoin network handle?
- What is the Lightning Network?
- What is a fork?
- Soft fork
- Hard fork
What is the expansion capability?
Capacity expansion is used to measure whether the system can meet the increase in demand. If the network is overloaded with too many requests, you can optionally add a server. If you want your computer to run more intensive applications, you may choose to upgrade your computer's hardware.
In the context of digital currency, "scalability" describes whether the blockchain can be easily upgraded to handle more transactions.
Why does Bitcoin need to expand?
In order to handle daily payments, the Bitcoin system must be fast enough. So far, the Bitcoin network’s throughput has been relatively low, meaning the number of transactions each block can handle is quite limited.
As mentioned above, miners who submit valid blocks can receive transaction fees. This fee is paid by users to incentivize miners to write transactions into blocks.
Miners need to get returns from their investment in hardware and electricity, so they will prioritize transactions with higher fees. If the network has a backlog of pending transactions (mempool), fees will surge because users will need to offer high prices to attract miners. In extreme periods, the average handling fee has exceeded $50.
How many transactions can the Bitcoin network handle?
Based on the average number of block transactions, the Bitcoin network can currently handle approximately 5 transactions per second (TPS). This speed is much lower than centralized payment methods and is one of the costs of using decentralized currencies.
The Bitcoin system is not managed by a data center, and upgrades cannot be decided at will by a single organization, so the Bitcoin block size must be limited. Blocks can indeed accommodate 10,000 transactions per second, but such a setting will reduce the decentralization of the network. Full nodes need to download new block information every 10 minutes; if this process is too cumbersome, the node may choose to quit.
Bitcoin enthusiasts believe that if the system is to be used for payments, it needs to be effectively expanded through other means.
What is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is a Bitcoin scaling proposal. It is also called the "Second Layer" solution, which separates transactions from the blockchain; all transactions are recorded on the bottom layer and are processed by the underlying protocol.
The Lightning Network enables near-instant fund transfers for free, with unlimited throughput (as long as users have the ability to send and receive funds). The method of using the Bitcoin Lightning Network is that two participants lock a certain amount of Bitcoin in a special address; the address has a feature that the funds will only be unlocked when both parties agree.
At this point, both parties share a private ledger; the ledger can allocate balances on its own without informing the main chain. After the transaction is completed, the main chain can be notified, and the main chain protocol will update the balances of both parties to the transaction. In this process, both parties to the transaction do not need to trust each other. If either party attempts to cheat, the protocol automatically detects this and imposes penalties.
Such a payment channel only requires users to conduct a total of two on-chain transactions: the first is to recharge the address, and the second is to distribute funds. As a result, thousands of transfers were made between transactions. With future development and optimization, second-layer technology may become a key component of vast blockchain systems.
For more details on expansion and potential solutions, please refer to "Blockchain Scalability - Sidechain Technology and Payment Channels".
What is a fork?
Because the Bitcoin system is open source, anyone can edit it, such as adding new rules or deleting old rules according to different needs. However, not all editors are "created equal"; some updates will make nodes incompatible with the network, and some will cause backward compatibility.
Soft fork
Soft fork means that after the rules are changed, Nodes with new rules deployed can still interact with undeployed nodes. Take block capacity as an example: Assume that the original block capacity is 2MB; from now on, half of the network nodes will implement a new limit of 1MB block capacity, and will regard blocks that are too large as invalid.
Legacy nodes can still receive or broadcast blocks. In this case, the new network can cover all nodes regardless of the rule version.
As you can see from the animation below, new blocks with smaller capacity are accepted by old and new nodes. However, new nodes will not recognize 2MB blocks as they need to follow new rules.

Bitcoin’s Segregated Witness (also known as "SegWit") is a soft An example of bifurcation. This fork cleverly introduces a new format for blocks and transactions. Nodes that have not been updated can continue to receive block information, but do not participate in the verification of new transactions.
Hard fork
Hard fork is more troublesome. Suppose now half of the network nodes want to expand the block size from 2MB to 3MB. If a 3MB block is sent to a legacy node, the block will be rejected; because the legacy node rules clearly state that 2MB is the upper limit of valid blocks. At this time, the new and old versions of the network are no longer compatible, and the blockchain has two branches.

The black chain in the picture above represents the original blockchain, and the second Blocks are where hard forks occur. Since then, newer versions of nodes have begun to create blocks with larger capacity (green blocks). Older nodes did not recognize these blocks and developed in a different direction. The blockchain becomes two, and the common history ends at the second block.
At this time, there are two network protocols, each using different currencies. The balances of all accounts are cloned from the original records to the new chain; if a user owns 20 BTC before the fork, he will have an account on each of the two branches with balances of 20 BTC and 20 new BTC.
In 2017, the Bitcoin network experienced a controversial hard fork, similar to the above situation. A small number of users hope to expand the block capacity to increase throughput and reduce handling fees. Other users believe that the expansion strategy is inappropriate. In the end, the hard fork resulted in Bitcoin Cash (BCH), which became independent from the Bitcoin network and formed its own community and development path.
For more details about forks, please see "Hard Forks and Soft Forks".
Chapter 7: Participating in the Bitcoin Network
Content Tour
- What is a Bitcoin node?
- How do Bitcoin nodes work?
- Full node
- Light node
- Mining node
- How to run a Bitcoin full node?
- How to mine Bitcoin?
- How long does mining take?
- Who can contribute code to the Bitcoin system?
What is a Bitcoin node?
The term "Bitcoin node" is used to describe a class of programs that interact with the Bitcoin network in a specific way. A node can be a mobile phone running a Bitcoin wallet, or a dedicated computer that stores the complete record of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Nodes are divided into different types, each performing specific functions. All these nodes are the communication points of the network, communicating transaction and block information within the network to each other.
How do Bitcoin nodes work?
Full nodes
Full nodes are responsible for verifying whether transactions and blocks meet specific requirements (that is, whether they are valid). Most full nodes will run "Bitcoin Core" software--the reference implementation of the Bitcoin protocol.
"Bitcoin Core" is a program released by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. At the time, the program was simply named "Bitcoin". To avoid confusion, the name was later changed to "Bitcoin Core". Full nodes can also run other implementations, provided that the implementation is compatible with "Bitcoin Core".
Full nodes are the key to Bitcoin remaining decentralized. They are responsible for downloading, validating blocks and transactions, and broadcasting relevant information to the entire network. Since each full node independently verifies the authenticity of information, users do not need to rely on a third party to do anything within the network.
The full node that stores the complete record of the blockchain becomes a "complete archive node" ”. Some users discard old blocks to save storage space—the Bitcoin blockchain contains more than 200GB of transaction data.

Global distribution of Bitcoin full nodes. Image source: bitnodes.earn.com
Light nodes
The execution capabilities of light nodes It is not as good as a full node in terms of performance, but the resource requirements of the former are also relatively low. Users can access the network through light nodes without running all the functions of a full node.
Full nodes need to download all blocks and verify them one by one, while light nodes only need to download a part of each block (also called the "block header"). Although the block header is small in size, it contains enough information to allow users to view the specific block in which the transaction occurs.
Light nodes are ideal for devices that are limited by bandwidth or storage space. Therefore, light nodes are common in desktop and mobile wallets. Since verification is impossible, light nodes can only rely on full nodes.
Mining nodes
Mining nodes perform another additional task on the basis of full nodes. Task: Create blocks. As mentioned above, mining requires specialized equipment and software with the purpose of adding new data to the blockchain.
The mining node performs a hash operation on the collected pending transactions together with other information to obtain a numerical value. If the value is lower than the target threshold set by the protocol, the block is considered valid and can be broadcast to other full nodes.
If you want to mine independently, the miner must first run the full node function. Otherwise, miners cannot know the transaction information in the block.
If participants want to mine but are unable to run the full node function, they can connect to the server and obtain the required information. For example, mining pools (that is, cooperation with other nodes) only require one of the nodes to run full node functions.
For a breakdown of node types, please refer to What is a Node? 》.
How to run a Bitcoin full node
Full nodes benefit developers, merchants, and end users. By running the "Bitcoin Core" client on its own hardware, users' privacy and security are better protected, making the Bitcoin network more stable. If users use full nodes, they do not need to rely on anyone when participating in network interactions.
Some Bitcoin-oriented companies offer "plug-and-play" nodes, shipping pre-built hardware directly to users. Users simply plug in power to the hardware and start downloading the blockchain. This method may be more suitable for less technical users, but the cost is much higher than assembling the hardware yourself.
In most cases, an old desktop or laptop computer will suffice. However, computers used daily should not run full nodes to avoid serious constraints on running speed. As blockchain continues to grow, users must ensure that their devices have enough space to accommodate the complete blockchain record.
A 1TB hard drive can meet the data volume in the next few years, provided that the block capacity does not change significantly. Other hardware requirements include 2GB of RAM (generally more on most computers that come stock) and a lot of bandwidth.
After the hardware is ready, you can refer to bitcoin.org's "Full Node Operation Guide" for specific setup steps.
How to mine Bitcoin?
When Bitcoin was in its infancy, laptop computers were sufficient for block creation. At the time, Bitcoin was little known and mining competition was almost non-existent. Since the network is not yet active, the protocol will naturally set a lower mining difficulty.
As the hash rate of the network increases, miners must upgrade their equipment to remain competitive. After multiple rounds of hardware transformation, the mining industry has finally entered the so-called "application specific integrated circuits (ASICs)" era.
As the name suggests, these devices are made for a specific purpose. They are very efficient but can only perform a single task. Therefore, a mining ASIC can be said to be a computer that can only be used for mining. In addition to Bitcoin mining, Bitcoin ASICs can also mine digital currencies with different algorithms.
Now, Bitcoin mining requires huge investment, including hardware and energy. As of this writing, a good mining rig is capable of performing 10 trillion operations per second. Along with high efficiency comes high energy consumption. Unless you have multiple mining machines and cheap electricity, it is difficult for ordinary miners to make a profit from Bitcoin mining.
However, with the right equipment, setting up a mining operation is fairly straightforward - many ASIC devices come with their own software. A common approach is to connect a mining machine to a mining pool and cooperate with others to mine. If the mining pool successfully creates a block, the block reward will be distributed to the various cooperating miners in proportion to the hash rate.
Miners can also choose to min alone; the success rate of creating a block will be very low, but the miner can monopolize the block bonus.
How long does mining take?
There is no definite answer to this question because mining time is affected by many factors, such as the amount of electricity and hash rate that the miner can utilize. In addition, the actual cost of operating mining equipment also needs to be taken into account.
To get a rough idea of Bitcoin mining profits, you might as well use a mining computer to estimate costs.
Who can contribute code to the Bitcoin system?
The "Bitcoin Core" software is open source, which means anyone can contribute code. Users can propose new features, which are reviewed and added to the more than 70,000 lines of code; they can also report bugs, translate documentation, or improve documentation.
Software changes require strict review. After all, the system handles hundreds of billions of dollars in funds and must ensure there are no loopholes.
If you are interested in participating in Bitcoin code contribution, you may wish to check out the blog of developer Jimmy Song or the official website of "Bitcoin Core".


 Forum
Forum Finance
Finance
 Specials
Specials
 On-chain Eco
On-chain Eco
 Entry
Entry
 Podcasts
Podcasts
 Activities
Activities
 OPRR
OPRR
