Introduction
Cryptocurrency has significant characteristics and is not susceptible to hacker attacks or shutdowns. Everyone can transfer value around the world through cryptocurrencies without the need for third parties to intervene.
Ensuring that these characteristics remain unchanged comes at a huge cost. Throughput is limited due to the large number of nodes running the cryptocurrency. Therefore, although it is a technology aimed at popularizing the public, the transaction volume per second (TPS) that the blockchain network can handle is relatively low.
In order to break the inherent limitations of blockchain technology, various scalability solutions have emerged to increase the number of transactions that the network can handle. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into one of the extensions to the Bitcoin protocol, the Lightning Network.
What is the Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network runs on top of the blockchain and is designed to accelerate peer-to-peer transactions. The use of this network is not limited to Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies such as Litecoin are also integrated into it.
We may be confused, what does "on top of the blockchain" mean? Lightning Network is the so-called off-chain or Layer 2 solution. Individuals can transact via the network without recording each transaction in the blockchain.
The Lightning Network is independent of the Bitcoin network and has independent nodes and software, but it still needs to communicate with the main chain. To move in and out of the Lightning Network, special transactions need to be created in the blockchain.
An individual’s first transaction is actually establishing a smart contract with other users. We’ll get into more details later. For now, let’s first think of smart contracts as private ledgers shared with other users. Users can write multiple transactions in this ledger. These records are only visible to users and counterparties, and based on the characteristics of the settings, both parties cannot falsify.
This kind of mini ledger is called a "channel". For example, Alice and Bob each invest 5 BTC into the smart contract. Each has a balance of 5 BTC in their channel at the moment. Then, Alice writes "Pay 1 BTC to Bob" in the ledger. Now, Bob has 6 BTC and Alice has 4 BTC left. Bob later sends 2 BTC back to Alice. After the balance is updated, Alice has 6 BTC and Bob has 4 BTC left. They can keep doing this for a while.
Any party can publish the current status of the channel to the blockchain at any time. At that time, the balances at both ends of the channel are allocated to the respective on-chain addresses of both parties.
As the name suggests, Lightning Trading is lightning fast. No need to wait for block confirmations, pay out as quickly as your internet connection allows.
Why is the Lightning Network necessary?
As of now, the Lightning Network (or "LN" for short) seems to be the most reasonable way to deal with the scalability of the Bitcoin blockchain. Coordinating changes in such a large ecosystem is tricky, with risks such as hard forks and potentially catastrophic vulnerabilities. Securing huge amounts of value is a top priority, and experiments are extremely dangerous.
If experimentation is to be removed from the blockchain, more flexibility is necessary. A slight error in this way will not have a substantial impact on the Bitcoin network. A Layer 2 solution would not undermine any of the security assumptions that have kept the protocol running for more than 10 years.
Moreover, there is no need to change the usual way of operating. In this way, the end user's on-chain transactions continue as usual, and now there are more off-chain transaction options.
There are many benefits to using the Lightning Network. We will highlight the following points.
Scalability
Bitcoin blocks are created approximately every ten minutes and can accommodate a limited number of transactions . Block space is a scarce resource, so users must bid against each other to ensure that their transactions are included in the block space in a timely manner. Miners’ primary concern is getting paid, so they prioritize including transactions with higher fees.
Assuming there aren't multiple users trying to send funds at the same time, this won't actually be a problem. You can set the fee low so that the transaction is likely to be included in the next block. However, when everyone posts transactions at the same time, it causes the average fee to rise significantly, occasionally exceeding $5. At the height of the bull market in 2017, handling fees even exceeded $50.

Average Bitcoin transaction fees (in USD)
This may seem trivial for a Bitcoin transaction worth thousands of dollars. But micropayments are struggling. Who wants to pay an extra $5 for a $3 cup of coffee?
Using the Lightning Network still requires you to pay two fees, namely the cost of opening and closing the channel. Once the channel is opened, users and counterparties can conduct thousands of transactions for free. Once the transaction is complete, the final state is simply published to the blockchain.
From a macro perspective, if more people choose off-chain solutions such as the Lightning Network, the efficiency of block space usage will be improved. Small-amount, high-frequency transfers are conducted through payment channels, while block space is used for large-amount transactions and channel opening/closing. In this way, the number of user groups accessing the system increases, and scalability is further developed in the long term.
Micropayments
Bitcoin has a minimum transaction amount, which is approximately 0.00000546 BTC. At the time of writing, it was equivalent to about four cents. This is already a small amount, but the Lightning Network has pushed the transaction limit even lower. Based on the current smallest unit, it is 0.00000001 BTC, or one satoshi.
The Lightning Network is more attractive for micropayments. At the cost of regular transactions, sending small amounts on the main chain seems impractical. Within the channel, however, tiny fractions of Bitcoin can be sent for free.
Micropayments lend themselves to numerous use cases. Some predict that micropayments will become an effective alternative to the subscription service model, whereby users only pay a small amount for each use of the service.
Privacy
The second benefit of the Lightning Network is that user information is more confidential. Each party does not need to diffuse its own channel information on the network. The blockchain may show "This transaction opens a channel", but the details of the transaction will not be disclosed. If a participant chooses to make the channel private, the transaction progress will only be visible to the participant.
Assuming that Alice and Bob share a channel, and Bob shares another channel with Carol, Alice and Carol can send payments to each other through Bob. If Dan establishes a connection with Carol, Alice can also send him a payment. Imagine extending this model to a vast network of interconnected payment channels. According to this setting, as long as the channel is closed, it is impossible to determine who Alice sent funds to.
How does the Lightning Network work?
We have explained how the Lightning Network relies on channels between nodes at a high level. Now let’s study the underlying specific principles.
Multi-signature addresses
Multi-signatures (or "multisig" for short in English) are used for multiple Private key payment address. Once users create a multi-signature, they can specify the number of private keys required to pay funds and sign transactions. For example, the 1-out-of-5 scheme means that five keys generate a valid signature, and only one key is needed to sign a transaction. The 2 out of 3 solution means that if there are three keys, two of them are required to pay the fee.
To provision a Lightning Network channel, participants need to lock funds in a 2-out-of-2 scheme, that is, only two private keys are needed to sign the transaction, and two private keys are also required to transfer tokens. Let's go back to the Alice and Bob example. They were going to have to pay each other a lot of money over the next few months, so they decided to open a Lightning channel.
First, they each deposited 3 BTC into the shared multi-signature address. It should be emphasized that Bob cannot transfer funds out of the address without Alice's consent, and vice versa.
They only need to leave a record when adjusting the balances on both sides. Both parties each have an initial balance of 3 BTC. If Alice wants to pay Bob 1 BTC, why not just note that Alice has 2 BTC and Bob's balance is 4 BTC? This way the record can track the balance before a decision is made to actually transfer the asset.
This approach works, but what’s the secret? In fact, more importantly, does this make it easier to cooperate with each other? Assuming that Alice ends up owning 6 BTC and Bob is left with nothing, then Bob will not lose anything by refusing to release the funds (perhaps all he loses is his friendship with Alice).
Hash Timelock Contract (HTLC)
The above system is very boring and monotonous, and is inconsistent with the current trusted Compared to the settings, there is nothing outstanding. The mechanism we introduce next can enforce the "contract" between Alice and Bob, which will be much more interesting. If one party does not play by the rules, the other party can take remedial action and remove funds from the channel.
This mechanism is called "Hash Time Lock Contract", or abbreviated as "HTLC". This term may sound intimidating, but it’s actually a very simple and easy-to-understand concept. It combines the two technologies of hash lock and time lock to take remedial measures against various uncooperative operations in the payment channel.
Hash lock is a condition added to the transaction. Specifically, you need to prove that you know a certain secret before you can use funds. The sender hashes a piece of data and sends the transaction with the hashed value to the receiver. The recipient can only use the funds if it provides the initial data (i.e. secret) that matches the hash value. The only way this data can be obtained is by the sender.
Time lock is a restriction that prevents funds from being used before a specific time. It can specify a specific time or a specific block height.
Hash Time Lock Contract (HTLC) is created by combining hash lock and time lock. In practical applications, Hash Time Lock Contracts (HTLC) can be used to create conditional payments, where the recipient must provide a secret before a certain time, otherwise the sender will withdraw the funds. The following explanation will be easier to understand through examples. So, let's get back to Alice and Bob.
Opening and closing channels
We gave an example before, imagine that Alice and Bob just A transaction is created where both parties deposit funds to a shared multi-signature address. But these transactions have not been published to the blockchain yet! We need to do one thing first.

Three tokens from Bob, and three more tokens It comes from Alice.
Remember, the only way to get these tokens out of the multisig is for Alice and Bob to co-sign the transaction. If Alice wants to send all six tokens to an external address, Bob needs to approve it. She first initiated a transaction, specifying "Send six Bitcoins to this address", and then added her signature.
If she tries to publish the transaction immediately without Bob's signature included in it, the transaction is invalid. Alice must first hand over the incomplete transaction to Bob. After he signs, the transaction becomes effective.
So far, we have not established a mechanism to urge everyone to conduct honest transactions. As mentioned earlier, if the counterparty refuses to cooperate, funds are completely trapped. Let's take a look at the mechanisms to prevent such situations. This mechanism involves multi-step operations, please be patient as we introduce them one by one.
Each party provides a secret, which we call "As" and "Bs". Once both parties reveal their secrets, the consequences will be disastrous. Therefore, they have to keep it a secret for now. The two secrets generate their own secret hash values, namely h(As) and h(Bs). This way the two parties don't need to share secrets, just hashes with each other.

Alice and Bob share the secret hash value with each other.
Alice and Bob also need to create a series of commitment transactions before publishing the first transaction to the multi-signature address. That is, remedies to prevent the other party from seizing funds.
If you think of the channel as the mini ledger we mentioned before, then the commitment transaction is an update to the ledger. Whenever a new set of commitment transactions is created, the funds of two participants are rebalanced.
Alice's transaction has two outputs, one pays the address she owns, and the other locks in the new multi-signature address. She signed it and handed it to Bob.
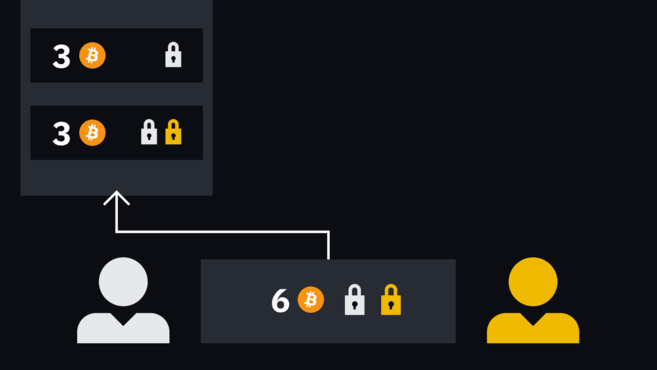
Alice’s transaction has two outputs, one to herself address, and the other to a new multi-signature, which requires Bob's signature to take effect.
The situation is the same for Bob, one output pays himself, and the other pays other multi-signature addresses. He signed it and handed it to Alice.

Two similar incomplete transactions.
Generally speaking, Alice can add a signature to the transaction to Bob to make the transaction effective. However, we noticed that these spending funds came from 2-out-of-2 multi-signatures that have not yet been allocated. This is similar to trying to write a check from an account that currently has a zero balance. Therefore, these partially signed transactions can only be used after multisig is up and running.
The new multi-signature address, the destination for the 3 BTC output, has some features. Let's take a look at the incomplete transaction signed by Alice to Bob. Multi-signature output can be used under the following conditions:
- Both parties can cooperate to sign the transaction.
- Due to the time lock, Bob can spend by himself after a period of time.
- If Alice knows Bob’s secret Bs, she can use the funds.
For the transaction from Bob to Alice:
- Both parties can cooperate to sign the transaction.
- Alice can spend money by herself after a period of time.
- If Bob knows Alice’s secret As, he can use the funds.
Please remember that neither party knows the other's secret, so point 3 is temporarily unachievable. Another note is that once one party signs a transaction, the counterparty has immediate access to funds because no conditions are placed on their outputs. The signatory needs to wait until the time lock expires before he or she can spend the funds on his or her own, or cooperate with the other party to spend the funds directly together.
All the best! You can now publish the transaction to the original 2-out-of-2 multi-signature address. This is safe because you can recover your funds if the counterparty abandons the channel.
After the transaction is confirmed, the channel will be up and running. The first pair of transactions shows the current state of the mini-ledger. At this time, the ledger pays 3 BTC to Bob and 3 BTC to Alice.
When Alice wants to make a new payment to Bob, the two will create two new transactions to replace the first set of transactions. The operation method is exactly the same, the transaction will be signed by each party half. It's just that Alice and Bob have to give up their old secrets first and exchange new hashes for the next round of transactions.
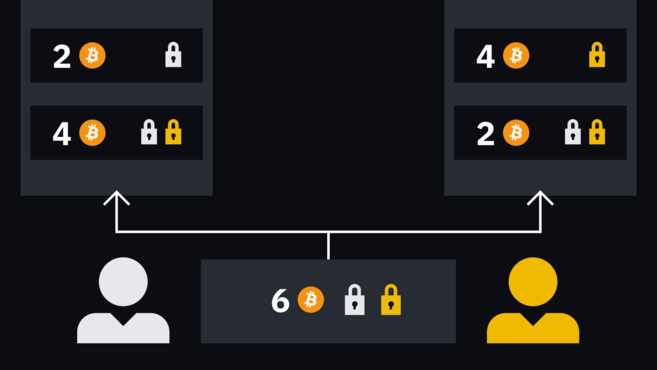
For example, Alice wants to pay Bob 1 BTC, Two new transactions will deposit 2 BTC to Alice and 4 BTC to Bob. This way, the balance will be updated.
Both parties can sign and publish the latest transaction at any time and complete "settlement" on the blockchain. However, the party signing the release needs to wait for the time lock to expire, and the other party can spend the fee immediately. Remember, if Bob signs and publishes Alice's transaction, she can have an unconditional output.
Both parties can reach a consensus and close the channel at the same time, that is, cooperation closing. This is the most convenient way for funds to return to the chain. However, if one party does not respond or refuses to cooperate, the other party can withdraw the funds after the time lock expires.
Want to start your cryptocurrency journey? Go to Binance and buy Bitcoin now!
How does the Lightning Network prevent fraud?
We may notice an attack vector here. Assuming Bob's current balance is 1 BTC, what can be done to prevent him from posting an old transaction with a higher balance? After all, he already got the semi-signed transaction from Alice, he just needs to add his signature and publish it, right?
Nothing can stop him from doing this. But if he did, he could lose his entire balance. Assume that he did post an old transaction that paid 1 coin to Alice and 5 coins to the multi-signature address we mentioned earlier.
Alice will receive the tokens immediately, but Bob must wait until the time lock expires before spending from the multi-signature address. Do you remember that we mentioned above that there is another condition that must be met before Alice can use the same funds immediately? She needed a secret that she didn't have at the time. But now she knows the secret - the second round of transactions has just been created and Bob leaked the secret.
While Bob can only wait for the time lock to expire, Alice can remove all the funds. This punitive mechanism ensures that participants do not attempt to cheat, otherwise the counterparty will receive their tokens.
Channel payment
We have talked about this problem before. Connections can be established between channels, otherwise lightning The network cannot effectively support payment functions. Imagine if we would actually deposit $500 into the same coffee shop just to have a cup every day for the next few months?
In fact, there is absolutely no need to do this. Alice and Bob have opened a channel, and Bob and Carol have also established a channel, so Bob can pay them both through the channel. By crossing multiple "hops" in this way, Alice can pay everyone on the path.

In this case, Alice can be reached through multiple channels Frank's place. In actual operation, she will definitely choose the most convenient channel.
Intermediary institutions play a certain role in the channel and will charge a small fee, but it is not mandatory. The Lightning Network is still in its emerging stage, and the charging market has not yet taken shape. Many expect to be able to charge fees based on liquidity.
In the basic chain, users need to pay fees based on the occupied block space, but have nothing to do with the value transferred. That is, paying $1 costs the same as paying $10 million. In contrast, the Lightning Network has no block space.
However, there is a concept of local balance and remote balance. Local balance refers to the amount that one party can "push" to the other end of the channel, while remote balance refers to the amount that the counterparty can push back to the local party.
Let’s give another example. Let's take a closer look at one of the above paths: Alice <> Carol <> Frank.

Every user’s before and after Alice transfers 0.3 BTC to Frank balance.
Alice <> Carol and Carol <> Frank The paths each have a total capacity of 1 BTC. Alice's local balance is 0.7 BTC. When everyone settles in the blockchain at this time, Alice receives 0.7 BTC and Carol receives the remote balance of 0.3 BTC.
Suppose Alice wants to send 0.3 BTC to Frank, she will push 0.3 BTC to the Carol channel side. Carol then pushes 0.3 BTC from her local balance to Frank via the channel. Ultimately, Carol's balance remains the same: +0.3 BTC from Alice and -0.3 BTC sent to Frank cancel each other out.
Carol does not lose value by acting as Frank's intermediary, but her own flexibility in managing funds becomes worse. It can be seen that she can currently spend 0.6 BTC in the channel with Alice, but can only spend 0.1 BTC at the end of the channel with Frank.
We imagine a situation where Alice is only connected to Carol, while Frank is connected to a wider network. Previously, Carol could send a total of 0.4 BTC to others through Frank, but now she only has 0.1 BTC at one end of the channel to push out.
In this case, Alice is actually cannibalizing Carol's liquidity. Without any incentives, Carol didn't want to put herself at a disadvantage. Therefore, she may propose "For every 0.01 BTC output from my channel, I will charge 10 satoshis". In this way, the higher the local balance Carol discards in the "stronger" path, the more she earns.
As mentioned before, there is no de facto fee requirement here. Some people are not worried about the liquidity getting worse, while others just want to open a channel directly with the recipient.
Limitations of the Lightning Network
If it turns out, the Lightning Network can give Bitcoin all the scalability When the problem is solved, everyone is happy. Unfortunately, the Lightning Network has shortcomings that hinder its development.
Usability
For beginners, Bitcoin is not the most intuitive system, addresses, fees Wait, it may be confusing. However, the wallet abstracts away these complex contents and provides users with operations that are similar to existing payment systems. We can let others download the smartphone wallet and send them tokens. This way they will be more than willing to complete the operation.
The Lightning Network currently cannot do this, and its smartphone app selection is still very limited. Generally speaking, Lightning Network nodes require access to Bitcoin nodes to be fully used.
After setting up the client, the user still needs to open the channel to make payment. This process is very time-consuming, especially when newcomers are exposed to concepts such as "inbound/outbound capacity" and are confused.
Therefore, the Lightning Network needs to be continuously improved to lower the barriers to entry and allow users to have a smoother experience.
Liquidity
A major criticism of the Lightning Network is that users’ transaction capabilities are limited. Personal spending cannot exceed the amount locked in the channel. If someone wants to spend all funds and transfer all funds from the channel to the remote balance, the channel must be closed. Alternatively, passively wait for others to pay through the channel, but this is not ideal.
Personal paths are limited by the total channel capacity. Take the previous Alice <> Carol <> Frank as an example. If Alice and Carol's channel has a capacity of 5 BTC, but Carol and Frank only have a capacity of 1 BTC, then Alice can never send more than 1 BTC. Even so, all balances must be on the Carol side of the Carol <> Frank channel to ensure the normal operation of the Lightning Network. This severely limits the amount of funds that can be transferred through Lightning Network channels, which in turn affects the usefulness of the network.
Centralized hubs
Based on the problems mentioned above, some people worry that such a network will spawn a large number of "Hubs" are large entities with strong liquidity and close connections that allow all large payments to pass through these entity channels.
Obviously, this development momentum is not a good sign. Centralized hubs cripple the system because taking these entities offline severely disrupts relationships between users. Additionally, with only a few points being traded, the risk of censorship increases.
The current status of the Lightning Network
As of March 2022, the Lightning Network is operating normally and has more than There are 35,000 online nodes, more than 85,000 active channels, and the capacity exceeds 3,570 BTC.

Global distribution of Lightning Network nodes. Source: explorer.acinq.co
Among the many different node implementations, Blockstream’s c-lightning, Lightning Labs ’s Lightning Network Daemon and ACINQ’s Eclair are particularly popular. Targeting less tech-savvy users, many companies have launched plug-and-play nodes. Users only need to plug in their device to start using the Lightning Network.
Summary
The Lightning Network mainnet was launched in 2018, although many believe it is still in a testing phase , but the network has shown amazing development momentum.
Currently, only users with a certain level of technical proficiency can operate Lightning Network nodes, so the network still needs to overcome some usability hurdles. With the vigorous development of the network, the barriers to entry are gradually lowering.
As long as the problem is successfully resolved, the Lightning Network will become an integral part of the Bitcoin ecosystem, greatly improving scalability and transaction speed.


 Forum
Forum Finance
Finance
 Specials
Specials
 On-chain Eco
On-chain Eco
 Entry
Entry
 Podcasts
Podcasts
 Activities
Activities
 OPRR
OPRR
