Chapter
Cryptocurrency Basics
How does blockchain work?
How to invest in cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrency FAQ
Chapter 1 - Cryptocurrency Basics
Table of Contents
What is Cryptocurrency?
What is unique about cryptocurrencies?
Why is it called “cryptocurrency”?
What is public key cryptography?
Who invented cryptocurrency?
What is the difference between cryptocurrencies and tokens?
What is a digital currency wallet?
What Is it a cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency (English abbreviation "crypto") is a digital currency that individual users can use as a medium to operate in a digital environment. Transfer economic value.
You may be wondering how this system differs from PayPal or digital banking apps on your phone. On the surface, their uses seem to be the same—paying friends, shopping on favorite websites, etc. are all common use cases. However, the underlying operating principles of the two are quite different.
What is unique about cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrencies are unique in many ways. However, its most important function is to serve as an electronic cash system that does not belong to any party.
High-quality cryptocurrency will have the characteristics of decentralization. No central bank or subset of users can change the rules without consensus. Network participants (nodes) establish communication with other participants by running software and share information with each other.
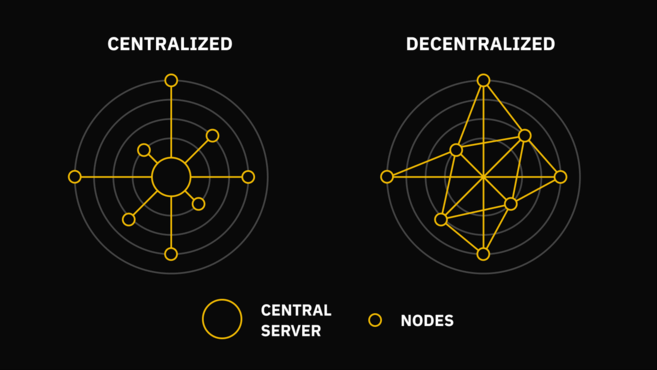
Comparison of centralized and decentralized trading platforms.
On the left is a system commonly used by banks. Users must communicate through a central server. The system on the right has no hierarchy: nodes are connected to each other and pass information to each other.
Cryptocurrency networks are decentralized and can effectively resist service interruptions or censorship. On the contrary, simply interrupting the main server can bring down the centralized network. If a bank's database is wiped and there are no backups, it can be difficult to determine a user's balance.
In the cryptocurrency world, nodes keep a copy of the database. Everyone can act as a server on their own and play an effective role. Each node can be offline, but its paired node can still capture information from other nodes.
Therefore, cryptocurrencies can circulate around the clock, allowing value to be transferred anytime and anywhere without the intervention of intermediaries. Therefore, we often call it permissionless: anyone can transfer money as long as they are connected to the Internet.
Why is it called "cryptocurrency"?
The term "cryptocurrency" is composed of cryptography and currency compound word. This is because cryptocurrencies extensively use encryption technology to protect transactions between users.
What is public key cryptography?
Public key cryptography lays a solid foundation for cryptocurrency networks and is the technical backing for users to send and receive funds.
In the public key cryptography scheme, you have a public key and a private key . The essence of a private key is a huge number that no one can guess. This number is often beyond imagination.
For Bitcoin, guessing the private key is equivalent to accurately predicting the outcome of 256 coin tosses. Today's computers alone will not be able to crack it even when the universe is heat dead.
As the name suggests, the private key must be kept properly no matter what. In addition, the public key can be generated from the private key. The latter can be sent safely to anyone. But the private key cannot be obtained by reverse engineering the public key.
You can also create a digital signature by signing data with your private key. This is similar to signing a document in the real world. The main difference is that anyone can compare the signature with a matching public key to determine whether the signature is valid. This way, users don't have to expose their private keys but can still prove ownership.
In the field of cryptocurrency, funds can only be spent if you get the corresponding private key. When you open a transaction, you will announce your transfer of currency to the network. The specific content will be announced through messages (i.e. transactions). The message is signed and added to the cryptocurrency database (blockchain). As mentioned above, a private key is required to create a digital signature. Additionally, since the database is completely open, anyone can verify that your transaction is valid by checking the signature.
Who invented cryptocurrency?
Various digital cash schemes have been launched over the years, with the first cryptocurrency being Bitcoin, which was launched in 2009. Its creator is a person or group of people under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. To this day, their true identities remain a mystery.
Bitcoin has spawned a large number of cryptocurrency "latecomers" - many of them competitors, and other products are trying to integrate Bitcoin Features not available. Today, in addition to conventional sending and receiving funds, many blockchains also support the use of smart contracts to run decentralized applications. Ethereum is perhaps the most popular example of this type of blockchain.
What is the difference between cryptocurrencies and tokens?
At first glance, there seems to be no difference between cryptocurrencies and tokens. Both are traded via exchanges and can be transferred between blockchain addresses.
Whether used as a medium of exchange, a means of saving value, or both, cryptocurrencies can only be used as funds . The function of each unit is homogeneous, that is, the value of the same currency is exactly the same.
Bitcoin and other early cryptocurrencies were just "money," but later blockchains tried to do more. For example, Ethereum provides more than just monetary functionality. It allows developers to run code (smart contracts) in a distributed network and create tokens for various decentralized applications.
Tokens can be used like cryptocurrencies, but with greater flexibility. You can mint millions of the same token, or choose a handful with unique properties. They can play a variety of roles, from digital receipts representing equity in a company to loyalty points.
In protocols that support smart contracts, the base currency (payment for transactions or applications) is separate from its tokens. For example, the native currency in Ethereum is Ethereum (ETH), which can only be used to create and transfer tokens within the Ethereum network. These tokens are created according to ERC-20 or ERC-721 standards.
What is a digital currency wallet?
Essentially, a cryptocurrency wallet is a vehicle for storing private keys. It can be a dedicated device (hardware wallet), an app on your computer or smartphone, or even a piece of paper.
Wallets are an integral interface for most users when interacting with cryptocurrency networks. Different types of wallets correspond to functional categories – obviously, paper wallets cannot sign transactions or display current prices in fiat currency.
If you consider convenience, software wallets (such as Trust Wallet) are undoubtedly the most suitable tool for daily payments. The security of hardware wallets is nearly unrivaled, effectively protecting private keys from prying eyes. Cryptocurrency users tend to store their funds in these two types of wallets.
Chapter 2 - How does blockchain work?
Directory
What is blockchain?
How are blocks added to the blockchain?
How does Ethereum mining work?
Can cryptocurrencies scale?
Who makes decisions for cryptocurrency software?
What Is it blockchain?
Blockchain is a special type of database in which data can only be added and cannot be deleted or changed. Transactions are regularly added to units called "blocks" (comprised of transaction information and other important metadata) within the blockchain.
We call this structure a "chain", and the metadata of each block contains a piece of information that connects it to The previous block is connected. Specifically, it contains the hash of the previous block, which you can think of as a unique digital fingerprint.
The probability that two pieces of data output the same value through the hash function is almost zero. So if someone changes an earlier block, its hash will change, causing a ripple effect in the hashes of subsequent blocks. On the other hand, if all subsequent blocks have changed, it can be easily inferred that the previous blocks have changed long ago.

The hash of each block is included in the next in the block. All blocks are connected into a chain to form a "blockchain".
The entire blockchain is downloaded locally by network participants. Remember how we introduced that public key cryptography can be used by anyone to verify transactions and signatures? After successfully receiving a block, the node performs several checks. Once an invalid value is found, the block will be "rejected".
If the block is valid, the node makes an exclusive copy of it and then propagates the original block to other nodes. The same operation will continue until the block is spread across the entire network. This process also applies to unconfirmed transactions – that is, the transaction has been broadcast, but has not yet entered the blockchain.
See also: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Blockchain Technology.
How is a block added to the blockchain?
If false financial information is accidentally entered, the integrity of the blockchain will be severely damaged. At the same time, this kind of distributed system has no administrator or person in charge to maintain the ledger, so how can we ensure that participants act with integrity?
Satoshi Nakamoto proposed a proof-of-work system in which anyone can propose a block to be added to the blockchain. In order to push blocks into the chain, users must work hard to guess the difficult problems set by the protocol at the expense of computing power.
Proof-of-work is time-tested and is undoubtedly an ideal way to reach consensus among users, but it is by no means the only solution. Developers are delving into alternatives such as proof-of-stake, and implementations are still being explored (although hybrid consensus mechanisms have been around for some time).
See also: "What is the blockchain consensus algorithm?" 》
How does Ethereum mining work?

The above process is called mining. If a miner finds a solution, the block constructed from it can be added to the blockchain. In return, they will be rewarded with the blockchain’s native currency.
The cryptographic puzzle that miners must solve requires repeatedly hashing data to ultimately generate a number below a certain value. Using a one-way function for hashing means that it is almost impossible to guess the "input value" when the "output value" is known. In contrast, when the "input value" is known, verifying the "output value" will be very simple. This way, all participants can verify that miners produce “correct” blocks and reject invalid blocks. Forging invalid blocks will not bring any rewards to miners and will only waste resources.
The result is some interesting game theory - fraudsters with ulterior motives waste funds and gain nothing, while honest and trustworthy miners behave properly , and ultimately made a huge profit. No malicious entity has the resources to attack a powerful network indefinitely. Therefore, in our vision, participants who hold resources will behave with integrity and receive reasonable returns on investment.
See also: "What is Cryptocurrency Mining?" 》
Can cryptocurrencies scale?
As you can see, distributed networks are inefficient. Unfortunately, cryptocurrencies can only be secure and censorship-resistant if all nodes can synchronize a copy of the blockchain. The less demanding it is to keep up, the easier it will be for new users to get involved.
Therefore, compared to adding a large block every five minutes, adding a small block every ten minutes is the ideal blockchain choose. The former requires nodes to run high-performance computers to stay in sync and pushes lower-performance devices offline sooner. This will lead to the continuous reduction of "peer nodes" in the network, leading to greater centralization.
However, the limitation of small blocks is the low transaction volume per second (TPS). During busy times, transactions may have to wait a while before being added to the blockchain. This will be inconvenient for people who want fast payments, but it is the price that must be paid for decentralization.
We call this problem the scalability dilemma. A highly scalable system can easily handle increased throughput with minimal negative impacts. Blockchains are poorly scalable - as mentioned earlier, simply increasing throughput through large blocks will seriously affect the overall operation of the distributed network.
To increase TPS without loss of network decentralization, off-chain expansion seems to be A feasible solution. It incorporates a range of centralized and decentralized solutions that allow transactions to be completed without being entered into the blockchain.
To learn more about off-chain scalability examples, please read "Blockchain Scalability: Sidechains and Payments" channel".
Who makes decisions for cryptocurrency software?
Cryptocurrency networks are optional and no one is forcing you to run software you don’t need. The code in the high-quality protocol is completely open source and supports users to verify the fairness and security of the system.
In general, anyone can contribute to the development of cryptocurrency. New features or code changes must be reviewed by the developer community before being agreed upon and officially released. Here, users can review the code themselves and choose whether to run it.
Some updates are backward compatible, that is, updated nodes can still communicate with earlier nodes. Most updates are not backward compatible. If early nodes are not updated synchronously, they can only "disappear" from the network. For more information, please read "Hard Forks and Soft Forks".
Chapter 3 - How to Invest in Cryptocurrencies?
Directory
Which cryptocurrency should I buy?
What should you learn before investing in cryptocurrencies?
Where to buy cryptocurrencies
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
-
Decentralized Trading Platform (DEX)
P2P Trading Platform
How to Buy Cryptocurrency
How to Buy Cryptocurrency on Binance
How to Buy Cryptocurrency on Binance Decentralized Exchange
How to buy cryptocurrencies on Binance P2P
Which cryptocurrency should I buy?
The decision is yours - you must do your own research (DYOR) and make decisions based on your personal analysis. Still, there are many tools you can use to make more informed decisions. For example, Binance Research studies market developments year-round, publishes insightful and analytical articles, and writes comprehensive reports for independent projects.
To be able to evaluate which cryptocurrency to buy, you must first understand how Bitcoin works. That’s why we’ve launched our What is Bitcoin guide!
What you should learn before investing in cryptocurrencies content?
Where should we start? There are many different methods of analyzing financial markets, and most professional investors generally use very different strategies. From a high-level analysis, investment evaluation is mainly divided into two major schools: fundamental analysis (FA) and technical analysis (TA).
Fundamental analysis is an asset value evaluation method based on economic and financial factors. Analysts using this method consider both macro and microeconomic factors, carefully studying the state of the industry or the companies (if any) that support the asset. In the cryptocurrency space, they also keep a close eye on public blockchain data (sometimes called “on-chain metrics”).
These metrics may involve the number of transactions, addresses, top holders, network hash rate, and a wealth of other information. This analysis is designed to value an asset and compare it to current valuations, ultimately transitioning into determining whether the asset is undervalued or overvalued.
However, we must recognize that cryptocurrencies are an emerging asset class that is booming. Fundamental analysis is of little use when valuing it. In short, a standardized framework for cryptocurrency valuation has yet to emerge, and most existing models fail to serve as benchmarks. The success or failure of a cryptocurrency project can depend on many factors that no current framework can explain.
Technical analysts are taking a different approach. Unlike fundamental analysts who determine the intrinsic value of an asset, technical analysts evaluate trades and investment opportunities based on historical trading activity. They pay close attention to price movements, chart patterns, indicators and use a variety of charting tools to assess the strength of market trends. Essentially, technical analysts believe that historical changes in an asset's price are strong indicators of future price movements.
Technical analysis can be applied to almost all financial markets that provide historical data and is widely favored by cryptocurrency traders.
Which method is more effective? Since both methods have their own advantages, we might as well approach them both. Most market analysis tools are most effective when used in conjunction with other tools. No matter what the situation is, being vigilant about financial risks and doing a good job in risk management are top priorities, and personal investments should never exceed the risk tolerance range.
Where to buy cryptocurrencies
There are many ways to buy cryptocurrency. First, fiat currency needs to be exchanged for cryptocurrency. You can then choose to hold, trade other cryptocurrencies or earn interest on loans. Let’s take a look at the different types of cryptocurrency trading platforms.
Centralized Exchange (CEX)
Cryptocurrencies are usually decentralized, you may feel The concept of a “centralized exchange” is confusing. Simply put, a centralized exchange is an online platform that facilitates transactions by connecting buyers and sellers.
The specific operating principle is that users deposit fiat currency or cryptocurrency into the trading platform and trade through the internal system. If you’re familiar with how cryptocurrency wallets work, you’ll know that in this case, the cryptocurrency is hosted by the exchange. Of course, funds can also be easily transferred to a personal wallet for safekeeping as needed.
Some people prefer to store funds on the trading platform to facilitate frequent transactions or access to funds. However, if the trading platform is hacked, user funds will be at risk.
Decentralized Trading platform (DEX)
Decentralized trading platform is different, it does not involve custody services. In fact, a more accurate name would be Non-custodial trading platform.
The following is the transaction process using a decentralized trading platform. You don't need to deposit funds into the trading platform wallet, you can trade using your personal wallet. Once a deal is made, the funds are transferred directly to the blockchain via magical smart contracts.
Decentralized trading platforms do not have any entity acting as a custodian, so some users believe that their security is better than that of centralized trading platforms. Another big advantage is that most decentralized exchange platforms do not ask users to provide any personal information other than their blockchain wallet address. At the same time, self-keeping of funds requires the accumulation of certain technical knowledge, and the responsibility lies entirely with the user.
P2P trading platform
Peer-to-peer (P2P) trading platform is also a channel to connect buyers and sellers, but it is different from CEX or DEX. It itself can only create transaction opportunities for buyers and sellers and will not interfere with transaction details. Therefore, the deposit and settlement method of each transaction is determined by negotiation between the buyer and seller.
How to buy cryptocurrency
How to buy cryptocurrency on Binance
Log in to your Binance account. New users please register first.
Log in to the cryptocurrency buying and selling portal.
Select the cryptocurrency you want to purchase and the currency you want to use for payment.
Select a payment method.
Follow the prompts to enter your card or bank details and complete identity verification.
Done! The purchased cryptocurrency will be credited to your Binance account.
How to buy cryptocurrencies on Binance decentralized exchange
Compared to other options , the decentralized trading platform is slightly more complex.
Before starting the operation, don’t forget to prepare the following tools:
A wallet that can be associated with Binance DEX (Trust Wallet is recommended).
Some BNB, used to pay transaction fees.
When you are ready, follow the instructions in our detailed guide to Binance DEX:
"How to create a wallet on Binance DEX"
"Binance DEX: Interface Wizard"
《Binance DEX: Access your wallet》
How to buy cryptocurrencies on Binance P2P
Log in to your Binance account. New users please register first.
Log in to the Binance P2P portal.
Choose to buy or sell.
Filter by currency, payment method, or other transaction requirements.
Select a listed currency that meets your requirements or publish your own currency for sale.
Chapter 4- Cryptocurrency FAQ
Table of Contents
Are cryptocurrencies legal?
Cryptocurrency is dead?
Are cryptocurrencies safe?
Are cryptocurrencies anonymous?
Are cryptocurrencies valuable?
Are all digital currencies cryptocurrencies?
What is the market capitalization of cryptocurrency?
Why do I need to pay transaction fees?
If the key is accidentally lost, can I still get my funds back?
What is the future of cryptocurrency?
Encryption Is the currency legal?
There are very few countries that explicitly prohibit the purchase, sale or saving of cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin and other virtual currencies are completely legal in the vast majority of countries around the world. Before participating in investing or spending, you must confirm whether the use of cryptocurrency is allowed in your jurisdiction.
Please note that each country has different regulations governing cryptocurrency activities. You may not violate any tax or compliance regulations.
Cryptocurrency is dead?

Cryptocurrency has been sentenced to death by the media hundreds of times over the past decade. However, today, it still operates and develops as it did in 2009. Of course, its volatility cannot be ignored, with prices ups and downs and frequent fluctuations. To those who are obsessed with making profits, bear markets can be frustrating.
However, “cryptocurrency is dead” is an absolute fallacy. Its user base is still expanding, and its technology and infrastructure are improving day by day.
With the continuous improvement of core technology innovation capabilities, Bitcoin and Ethereum will undoubtedly have a huge impact on the reshaping of the existing monetary system. influence and make it more consistent with actual development. Features such as immutability, censorship resistance, trustlessness, or near-instant transactions through the public currency system can completely subvert the operating mechanism of Internet economic activities.
Are cryptocurrencies safe?
Cryptocurrency carries certain risks. If you forget your bank account password, you can reset it through customer service. However, none of this will help if you forget or lose the private keys to access your cryptocurrencies. A reputable trading platform can reduce such risks - users entrust their funds to the platform and avoid the risk of losing their private keys.
Public key cryptography remains impregnable. Under the protection of advanced security measures, the chance of fund theft is significantly reduced, and online accounts frequently become victims of hacker attacks. Best practices for protecting against attacks include being aware of common scams (social engineering, phishing, etc.), always keeping private keys offline and backing them up in a safe location.
Are cryptocurrencies anonymous?
Your name is not associated with a cryptocurrency address - the latter is much like a random number and letter in the blockchain string. However, even if it is possible to become anonymous, care must be taken. Although you are acting under a pseudonym, your "on-chain identity" is still with you, but it is different from your real identity.
Through certain methods, users can associate IP addresses with activity. This virtually creates conditions for methods such as dust attacks and other analysis techniques to break anonymity. Don’t forget, the essence of blockchain is a huge public database. If you are concerned about personal privacy, you should try to avoid associating personal transactions with real names. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are not private by default, but methods such as currency mixing and CoinJoin can reduce the reliability of analytical heuristics.
A handful of cryptocurrencies (called privacy coins) use methods such as confidential transactions to obfuscate the funds in transactions Source, destination address and amount. They are more private by default, but are not completely resistant to deanonymization.
Are cryptocurrencies valuable?
In the financial system, value is a shared belief. As with anything of value, value is not an inherent property of cryptocurrency itself, but is artificially assigned. In other words, the value of something comes from everyone's consensus, not the thing itself. This is true whether the object of value is a precious metal, a piece of paper, or information in a database.
Despite this, some still believe that cryptocurrencies and Bitcoin can be regarded as scarce digital commodities. Because issuance speed and monetary policy are predictable, some believe Bitcoin may function as a store of value in the future, like gold. Bitcoin has been around for just over a decade, and whether it can stand the test of time in this regard remains to be seen.
Are all digital currencies cryptocurrencies?
The answer is no. Today, many countries and central banks are developing their own versions of digital currencies. However, these products are only "digital currencies". In fact, they are often collectively referred to as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC). These currencies are essentially digital versions of fiat currencies and do not offer most of the advantages of cryptocurrencies. They are legal currencies issued and declared by a central government and generally do not use distributed ledgers (such as blockchain) to save transaction records.
You may also have heard of Facebook Libra, another digital currency. The advantage of this project is that it plans to be built on an open source blockchain system. However, it will not be a permissionless currency like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Participants cannot use this digital currency with just a simple internet connection. What’s more, the project and the activities within it will be run and managed by an association of selected members.
Therefore, while also utilizing blockchain or cryptography principles, CBDC and other forms of digital currencies are not the same as cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. There are huge differences in currencies.
What is the market capitalization of cryptocurrency?
Price is not the only metric for measuring cryptocurrencies. Another equally important metric is how many units there are in a cryptocurrency, known as the supply.
Specifically, to assess the value of a cryptocurrency network, it is necessary to know the number of units in existence. This is called the circulating supply. Different cryptocurrencies have different issuance plans, so it is important to understand each network's issuance situation.
Market capital (or market capitalization) is equal to the unit price multiplied by the circulating supply.
Market capital = circulating supply * priceAs you might imagine, the market cap of a cryptocurrency network is a better reflection of the value in the network than the unit price. A network with a lower price but a larger circulating supply is likely to generate a higher total valuation (market cap) than a network with a higher price but a smaller circulating supply. In some cases, the opposite may be true.
However, it is worth noting that market capitalization does not represent the total amount of funds entering a specific market. For example, beginners often fall into the misconception that Bitcoin market capitalization represents the total amount invested in Bitcoin. This view is wrong because market capitalization depends on price and supply.
Why do I need to pay transaction fees?
If you send one Bitcoin to another address, the actual number of Bitcoins received will be slightly less than one. A small portion of this fee is paid to miners as a reward for adding individual transactions to the blockchain.
Many cryptocurrencies use similar mechanisms to incentivize users to protect network security. In a proof-of-work system, transaction fees are often bundled with newly minted tokens (Block Subsidy) to form the block reward.
The specific handling fee can be flexibly adjusted according to the urgency of the transaction. Rational miners will always seek high returns and often prioritize transactions with higher fees. You can view your current pending transactions to see the average fees and set your personal fees accordingly.
If the key is accidentally lost, I still Can the funds be recovered?
If the key is accidentally lost, the possibility of recovering it is slim. The biggest advantage of cryptocurrencies is the elimination of custodians and middlemen who manage financial transactions. But there is also a drawback, that is, all the responsibility will be borne entirely by you. Therefore, you must be extremely careful and never lose your private keys, which are the key to keeping a firm grasp on your funds.
What is the future of cryptocurrency?
How will cryptocurrencies develop in the future? This is a matter of benevolence and wisdom. Some people believe that Bitcoin will rise in the digital age, eventually replacing gold and disrupting the existing financial system. Others believe that cryptocurrencies will always be a secondary system that cannot grow beyond niche markets. Some people firmly believe that Ethereum will evolve into a distributed computer and become the mainstay of the new Internet.
Sceptics predict the industry will eventually collapse, while enthusiasts are relieved that cryptocurrencies remain a niche currency system. The results are indeed unpredictable, and it is too early to determine what will happen a year from now. But there is no denying that cryptocurrencies have huge growth potential.


 Forum
Forum Finance
Finance
 Specials
Specials
 On-chain Eco
On-chain Eco
 Entry
Entry
 Podcasts
Podcasts
 Activities
Activities
 OPRR
OPRR
